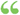 R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and A' is a collision factor that must have the dimensions of a frequency. R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and A' is a collision factor that must have the dimensions of a frequency.  Body Sensor Networks - Page 48edited by - 2007 - 494 pagesLimited preview Body Sensor Networks - Page 48edited by - 2007 - 494 pagesLimited preview - About this book
 | Floods - 1961 - 390 pages
...in which Zi is the valence, fa the transport number, and <Zi the activity of the ith ionic species ; R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and F is the Faraday. Each term in the summation represents the contribution made to the net emf by the diffusion... | |
 | J. Calvin Giddings - Science - 1984 - 334 pages
...Kp by Eq. (1), which converts V™ to the appropriate units of Kp [7]: V =2Zii2 fp_ g Tc p (1) where R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and AG is the partial molar free-energy change; Vg is the retention volume per gram of stationary phase... | |
 | Technology - 1998 - 122 pages
...conversion, X, by F ( -\ dG\ 1 r=dexp -1 , \RTdX) where the single constant /) is used for all reactions, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and G is the Gibbs energy. Using this equation, the chemical rate constants for each reaction can be related... | |
 | Craig A. Rogers - Technology & Engineering - 1994 - 1416 pages
...+ RT (Ci,t - Ci,,) = 0, (9) i = l where H.Network(V) is the osmotic pressure of a stress-free cell, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature and £,•,<, C,,,, determine the ionic concentration of species i in the cell and its outer environment,... | |
 | Victor N. Nikolaevskiy - Science - 1995 - 376 pages
...coefficients independent of pore pressure. For gases, relation (2.87) changes to ¿(g)= RTZ (3.11) Here, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and Z is the supercompressibility coefficient which accounts for the real deviation from the perfect gas... | |
 | Purdue Research Foun - Technology & Engineering - 1997 - 792 pages
...is the aqueous solution activity coefficient and yi is the immiscible solution activity coefficient, R is the universal gas constant. T is the absolute temperature and xw and x- are the mole fractions of solute in water and the organic liquid phase respectively.5 When... | |
 | Galen Wood Ewing - Science - 1997 - 1476 pages
...expression for the distribution coefficient AT of a solute between two phases is given by RT]nK = -AG0 where R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and AG0 is the excess free energy Now, AG0 = where AH0 is the excess free enthalpy, and A50 is the excess... | |
 | Hiroyuki Ohshima, Kunio Furusawa - Science - 1998 - 650 pages
...conduction. In these equations, K is the reciprocal Debye length, e is the permittivity, r\ is the viscosity, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and C is the electrokinetic potential (zeta potential). If there is some electrical conductivity in the... | |
 | Geoffrey Pritchard - Technology & Engineering - 1997 - 664 pages
...where s is the specific surface area of the filler, u is the cross-sectional area of the polymer chain, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and X is the ratio of filler volume fraction to matrix volume fraction. Most of the equations assume spherical... | |
 | Bernard Amadei - Rock mechanics - 1999 - 600 pages
...potential is defined as: + RT\naw (1) in which p is the pore pressure, Vw is the partial molar volume of water, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and aw is the water activity. The osmotic effect and associated pore pressure and stresses are calculated... | |
| |